How Toxic Links Undermine Authority and Visibility Across Search
Bad backlinks are one of the most common causes of lost rankings and manual penalties. In this guide, Stellar SEO explains how to identify, remove, and recover from toxic links while protecting your authority across Google and AI platforms.
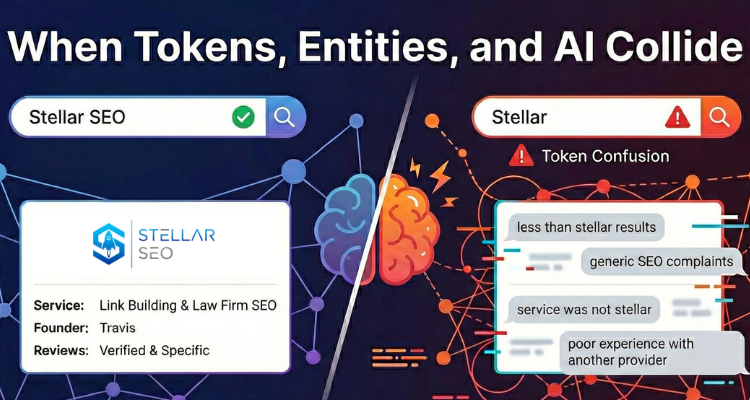
In 2025, bad backlinks do more than trigger ranking losses. They disrupt how search engines and AI systems interpret your brand’s authority and credibility.
Modern algorithms evaluate more than link count. They analyze link context, anchor diversity, and topical consistency to decide whether your site deserves to rank and be cited. When your backlink profile contains manipulative, irrelevant, or automated links, it erodes those trust signals.
This erosion impacts every discovery channel. Google’s algorithms reduce crawl priority and ranking potential, while AI platforms like Perplexity, Bing Copilot, and Google’s AI Overviews are less likely to reference your brand as a reliable source.
At Stellar SEO, we have spent more than a decade refining link risk management to address these issues before they become visible penalties. We analyze link velocity, anchor trends, and topical alignment to identify and correct toxic patterns before they damage your authority graph.
The result is a link profile that supports lasting visibility across both search and AI ecosystems, not one that quietly drags your reputation down.
What Are Bad Backlinks?
Bad backlinks are links that send the wrong trust signals. They often originate from irrelevant, spam-heavy, or automated sources, making your link profile look unnatural to search engines.
A few years ago, “bad backlinks” meant links from obvious spam sites. Today, it includes placements that look legitimate on the surface but fail contextually, such as unrelated guest posts, manipulative anchor text, or content that exists solely to manipulate rankings.
These links distort how Google and AI systems interpret your brand. Instead of reinforcing topical authority, they confuse entity relationships, weaken your credibility, and make your profile appear manufactured rather than earned.
Strong link profiles tell a consistent story about your expertise and relevance. Bad backlinks interrupt that story.
How Bad Links Damage Rankings and Authority
Toxic backlinks quietly erode performance long before a manual penalty appears. Search engines and AI systems interpret every link as a signal of trust. When those signals become distorted by manipulative or irrelevant backlinks, your site loses credibility in measurable ways.
1. Algorithmic Trust Decay
Google no longer measures value by PageRank alone. Its systems evaluate link context, domain patterns, and topical relationships to determine authenticity. When too many links appear forced or off-topic, they trigger domain-wide trust decay that reduces both ranking potential and crawl efficiency.
2. Suppressed AI Visibility
AI-driven platforms like Google’s AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, and Perplexity reference brands that show consistent, contextually clean link profiles. Toxic backlinks interrupt that consistency, causing your brand to disappear from generative summaries and answer boxes that now capture a growing share of search visibility.
3. Link Velocity Red Flags
Authority builds gradually through natural mentions. When a domain gains hundreds of links in a short time, especially from similar anchors or unrelated sites, it can look automated. These link velocity spikes often trigger filters that suppress growth even if no manual penalty occurs.
4. Reputational and Engagement Decline
Bad backlinks affect more than algorithms. When your brand appears on spam-heavy blogs, expired domains, or low-quality directories, it signals carelessness to users. That reduces engagement, lowers branded search demand, and weakens conversion rates.
A strong link profile tells a consistent story of expertise and relevance. A toxic one breaks that narrative, confuses both algorithms and users, and weakens every other SEO effort you invest in.
Case Study: National Mortgage Lender Manual Penalty Recovery
A national lender in the highly competitive mortgage market approached Stellar SEO after being hit with a manual penalty that eliminated their first-page visibility for major loan-related keywords. Their backlink profile was cluttered with spammy affiliate sites using dofollow links, low-quality lender directories, and other clear signs of link spam.
Over two months, our team manually reached out to hundreds of site owners to request link removals. We documented every outreach message and response, building a comprehensive record of the cleanup process. After removing a significant share of the toxic links through outreach, we finalized a disavow file for the remaining spam domains.
This complete documentation was submitted through Google Search Console, along with detailed proof of the cleanup process. The reconsideration request was accepted on the first attempt. Within weeks, the lender regained first-page rankings for one of their most competitive national keywords and saw a steady rebound in overall organic traffic.
This project shows how a deliberate, transparent cleanup approach focused on real outreach and documented action can reverse penalties and restore search authority in even the toughest markets.
Types of Bad Backlinks to Watch Out For
| Type | Common Risk |
| Spammy Blog Comments | Creates visible spam footprint |
| Paid Links | Triggers manual action if unlabeled |
| PBNs | Easily devalued network links |
| Hacked Domains | Association with malware |
| Sitewide Links | Pattern signals link selling |
| Over-Optimized Anchors | Causes trust decay and over-optimization flags |
Not all backlinks are helpful. Some create risk by signaling manipulation, automation, or poor relevance. The following are the most common sources of toxic links we uncover during audits and penalty recovery projects.
1. Spammy Blog Comments and Forum Links
Automated comment spam remains one of the oldest and most visible link manipulation tactics. Thousands of low-quality blogs and forums still allow users to drop keyword-stuffed links in comments. When this pattern repeats across multiple domains, it builds a clear spam footprint that weakens your trust signals.
2. Paid Links from Irrelevant or Low-Authority Sites
Paid links that are not labeled with rel=”sponsored” can lead to trust issues. Irrelevant placements on weak or public link-selling sites confuse search engines about your topical authority. Even if they do not trigger a manual action, they can still dilute your link quality and ranking potential.
3. Private Blog Networks (PBNs)
Private blog networks are groups of expired or recycled domains created to pass link equity. Their content is thin, their footprints are easy to detect, and they often share the same hosting or linking patterns. A handful of PBN links can undermine months of legitimate link-building progress.
4. Hacked or Repurposed Domains
When legitimate domains are hacked or later repurposed for spam, they sometimes continue linking to trusted websites. Those links become toxic by association. Being linked from a compromised or malware-infected domain signals risk and can hurt both visibility and reputation.
5. Sitewide Footer and Sidebar Links
Links that appear across every page of a site can look manipulative if they point to commercial pages. While one branded footer credit is fine, hundreds of repeating outbound links across unrelated domains often appear to be part of a link-selling scheme.
6. Irrelevant or Over-Optimized Anchor Text
Anchor text should look natural and fit the surrounding context. Repeating the same keyword-rich anchors across multiple unrelated placements signals over-optimization. Balanced profiles use a mix of branded, partial-match, and natural anchors that fit naturally within editorial content.
A strong link profile is not about removing every low-quality domain. It is about maintaining a clean pattern of relevance, context, and diversity that reflects genuine authority instead of manipulation.
How to Identify Bad Backlinks in Your Profile
Identifying toxic backlinks requires more than scanning a list of referring domains. It involves understanding the signals that influence how Google and AI systems interpret your site’s trust, authority, and relevance. While advanced audits take time and experience, there are practical ways to identify potential problems before they cause ranking loss.
Start by using tools like Ahrefs, Link Research Tools, or Google Search Console to review your backlink profile. Look for trends and patterns rather than individual links. The goal is to determine whether your site is earning natural mentions or accumulating links that appear manipulative or irrelevant.
Pay close attention to:
- Unnatural Link Growth: Review your link acquisition over time. A sudden spike in new referring domains, especially from unrelated industries or low-quality blogs, can indicate spam or automation.
- Anchor Text Patterns: Sort your backlinks by anchor text. If a small number of commercial phrases dominate, or if anchors sound forced, those links could distort your site’s authority signals. Proper anchor variation begins with content that naturally earns links, which is exactly what effective SEO copywriting services are designed to achieve.
- Referring Domain Quality: Open a sample of linking pages. If the content looks thin, filled with outbound links, or unrelated to your niche, those links likely offer no real value.
- Topical Consistency: Evaluate whether your links align with your subject matter. A personal injury lawyer receiving links from gambling sites, for example, sends conflicting signals to search engines. Strong internal relevance and topical alignment start with optimized page structure, which our on-page SEO services help establish before link building ever begins.
- Geographic Relevance: Links from regions where your business does not operate, such as large numbers of .ru or .cn domains, often appear in link spam patterns.
- Excessive Sitewide Links: Dozens or hundreds of footer or sidebar links from one domain can appear unnatural, even if the site itself is legitimate.
These checks help you understand where your backlink profile might look abnormal. If you begin noticing recurring patterns or clusters of questionable links, that is when a professional audit becomes essential.
A proper cleanup involves determining which links are harmless, which are dragging down trust, and which require outreach or disavowal.
Red Flags to Watch For
After reviewing your profile, you may recognize signs that indicate a deeper link issue. The following are the most common warning indicators that we find during link audits and penalty recovery projects:
- Overoptimized Anchors: When anchors repeat the same keyword-heavy phrasing across multiple sites, it suggests automation or a lack of editorial control. Natural links include varied anchors that match their context.
- Rapid Link Velocity: Healthy growth occurs over time as your brand earns mentions. A large, sudden increase in backlinks can suggest link buying, negative SEO, or automated generation.
- Toxic Neighborhoods: Links from low-quality domains, such as adult, gambling, or expired blog networks, can harm your authority by association. Search engines group sites into “neighborhoods,” and those neighborhoods influence how trustworthy your site appears.
- Single-Source Saturation: Hundreds of links from one domain, especially in templates or directory lists, create an artificial footprint. One or two high-quality mentions are fine; hundreds look manipulative.
- Irrelevant Content Links: Even if a linking site has good metrics, a backlink from unrelated content weakens topical authority. Relevance matters more than raw domain metrics.
- Unlabeled Paid or Sponsored Links: Paid placements that lack the proper “nofollow” or “sponsored” attribute violate Google’s link guidelines. These links often lead to manual penalties when detected.
Spotting one or two of these issues is not necessarily cause for alarm. However, when several appear together or in volume, it signals a deeper pattern that requires expert evaluation. A professional audit can determine which links pose real risk and create a plan for removal or replacement.
From there, we deploy a cleanup and rebuilding plan that restores balance through editorial placements, digital PR, and niche-specific authority links. Learn more about how our link building services create lasting growth while reducing link-related risk.
Google’s View on Link Schemes and Toxic Links
Google has consistently opposed link schemes, including buying links or establishing private blogging networks. However, the search engine’s tactics to combat low-quality content became more sophisticated in 2012, when the Penguin update was rolled out.
The Penguin update began to punish dangerous links while more strictly enforcing the Webmaster Guidelines. Through this algorithm, Google assumes that quality sites refer to other quality sites and that low-quality sites will link to one another.
Therefore, dofollow links from suspicious, deceptive, or spammy websites can lead to manual penalties or algorithmic devaluation.
In 2019, Google became more precise about backlinks, including considering no-follow links as suggestions or context. They also rolled out more specific rel tags for these links, such as for sponsored links and user-generated content.
Manual Actions and Algorithmic Filters
Manual actions are used for sites that explicitly violate SEO best practices, including those with thin content, spammy backlinks, or deceptive linking practices. If you have a manual action, some or all of your site will not appear in search results, even relevant ones.
You can check whether you have had a manual action on Search Console. The action report will explain which pages are affected and why, and it will provide an action plan for resolving the issue. Typically, a manual action is only issued if you have been participating in link schemes or buying backlinks.
To fix a manual action, you solve the issues and submit a reconsideration request. Google will then review the changes and either remove the penalty or demand further action.
Manual actions are easier to bounce back from, but algorithmic filters can take years to resolve. This is because there is no way to request a reevaluation when the algorithm has determined that your site may contain spammy content.
You will need to work with an SEO expert who can determine whether you have been algorithmically devalued, what must change, and how to complete the project. Unfortunately, Google has been relying more on algorithmic devaluation than manual action in recent years, making it even more challenging to boost your rankings after an issue.
Disavowing Links: When and How to Do It
Google’s Disavow Tool allows you to tell crawlers to ignore certain links. Essentially, you turn them into nofollow backlinks, even if they were originally dofollow links. This is a last resort if you can’t ask a webmaster to remove the link for you, and it should only be done if you have no other option. We only use this tool for manual link penalty recovery or if a manual link penalty is imminent.
To disavow, you will create a .txt file with all the links that you would like removed. You can choose specific URLs or blacklist entire domains, depending on your needs. Navigate to the Disavow Links tool in Search Console and upload your file. Google will then review the file and take action, typically within a couple of weeks.
However, a disavow request is only a strong suggestion, not a guaranteed removal. Google may still decide that some links provide important context for your site and lower your rank accordingly.
Link Removal Outreach Strategies
Successful link cleanup requires more than submitting a disavow file. At Stellar SEO, we use a structured outreach process that prioritizes manual link removal whenever possible, because genuine effort and documentation carry significant weight in Google’s reconsideration process.
Before disavowing, we manually contact each referring domain to request link removal or a rel=”nofollow” update. Every message includes specific URLs, link locations, and context for why removal is necessary, making it easy for site owners to act quickly. This precision and transparency often lead to faster cooperation and cleaner outcomes.
We also track every outreach attempt, response, and removal in a central system to maintain complete visibility. This documentation serves two purposes: it keeps the process organized and provides verifiable proof of cleanup when submitting a reconsideration request in Google Search Console.
Our experience has shown that combining thorough manual outreach with a carefully targeted disavow file produces the highest success rate for penalty recovery and algorithmic trust restoration.
Tools to Help with Backlink Audits and Cleanup
The same tools you can use for link building can also be used to audit your site and identify dangerous links. Some of the best options include Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz.
Ahrefs’ backlink checker lets you review all links to your site, filtering them by domain rank so that you can find spammy domains. SEMrush’s tools work similarly, though it specifically searches for backlinks that may be lurking in your profile and provides suggestions for improvement.
Lastly, Moz’s Link Explorer lets you review things like anchor text and referring domain quality. This is crucial, as it can help you determine whether certain sites are using overoptimized anchor text that may be harming your rankings.
How Often Should You Audit Your Backlinks?
While link-building, you must regularly audit your profile to ensure that no toxic backlinks have shown up. Generally, you should conduct a quarterly review. However, audit frequency depends on factors like site size, niche, and link velocity.
If you have a large site, you will naturally have more link-building opportunities, which also means a higher likelihood of toxic backlinks. A monthly schedule may work best to stay on top of potential issues. Similarly, those in a larger or more competitive industry may face risks like black-hat campaigns that must be carefully monitored.
Link velocity also matters. If you have acquired numerous links in a short period, such as when your content goes viral, you should conduct more frequent audits and remain proactive.
How to Recover from a Link-Based Penalty
There are several steps to recovering from a link-based penalty:
- Review the manual action report to understand what happened and what Google suggests as a solution.
- Audit all your links. Check for toxic backlinks that may have slipped in.
- Contact the webmasters and ask that the links be removed. Failing that, use the Disavow Tool to remove all of them at once.
- Submit a reconsideration request. Details the steps you have taken to rectify the issue.
- Begin rebuilding trust with Google by practicing ethical link-building, manually contacting potential link partners, and regularly removing dangerous links.
Proactive Strategies to Avoid Bad Backlinks
The best way to avoid toxic backlinks is to take a proactive approach to link-building. Regular audits, thorough research, and ongoing monitoring ensure that you will not incur penalties or lose your high ranking.
Vetting All Link Opportunities
Before agreeing to any link placement, review the site’s authority, relevance, and traffic. Investigate the site’s backlinks to determine whether they may come from link farms or paid schemes.
Avoiding Low-Quality Guest Posts
Website owners believe that any exposure is beneficial, so they may accept guest post opportunities from spammy websites in the hope that it will improve their ranking. However, this can lead to toxic backlinks. If a suspicious site offers you a link in exchange for content, conduct thorough research and be prepared to decline.
Watching for Negative SEO Campaigns
These campaigns are a black-hat tactic designed to lower a competitor’s rank. This can include submitting the competitor’s link to a spammy website, embedding hidden links on private blogging networks, or spamming the site link on suspicious forums.
If you notice a large number of links from certain domains, consider whether this might be a negative campaign from a competitor. Research the domains and determine whether they have ever been associated with one of your competitors.
Creating Linkable Content That Attracts Editorial Links
Also known as link baiting, this approach focuses on making high-quality, original content that answers questions users may have. For example, you may create an “ultimate guide” to an industry topic, develop infographics, or publish original research.
Great content will naturally attract links from high-quality sources like news articles or industry journals. However, you’ll still need to regularly assess your link profile to ensure that no toxic backlinks have slipped in.
What to Do If You Suspect Negative SEO
Black-hat campaigns involve a competitor or other bad actors intentionally targeting your website by linking to it from suspicious sites. You can identify this by tracking your link velocity and monitoring traffic. Suspicious spikes or drops can suggest someone is directly targeting your site.
Set up Google Console Alerts to receive immediate notifications of manual actions or other suspicious activity. This can help you determine when the campaign started and which links may be involved.
You will then need to review your link profile and remove or disavow toxic links. In some cases, you must create a comprehensive disavow file that includes every toxic URL.
Because these campaigns are often associated with phishing or hacking attempts, add additional cybersecurity measures before contacting an experienced SEO expert like Stellar SEO.
Stellar SEO’s Approach to Link Risk Management
Stellar SEO has spent over a decade helping brands recover, rebuild, and futureproof their organic visibility through strategic link risk management. Our team has built more than 25,000 links, guided over 100 sites through manual penalty recoveries, and refined a process that balances precision link acquisition with long-term protection.
We don’t rely on automated tools or mass disavows. Every backlink is analyzed for intent, context, and potential risk. Disavowing links is always a last resort and reserved only for manual penalties or situations where one is imminent. In every other case, we focus on replacing weak links with stronger, earned placements that elevate your site’s authority.
Our process begins with a forensic backlink audit that identifies toxic link clusters, footprint risks, and algorithmic triggers. From there, we deploy a cleanup and rebuilding plan that restores balance through editorial placements, digital PR, and niche-specific authority links.
This isn’t just damage control. It’s a structured authority framework designed to stabilize rankings, restore trust, and strengthen your brand’s visibility across Google and AI-driven search systems.
With over a decade of proven results, Stellar SEO remains one of the most experienced teams in the industry at both penalty recovery and sustainable link growth. When you need precision, not panic, we’re the team other agencies call for help.
Why Experience Matters in Link Cleanup
Recovering from toxic backlinks is not about checking boxes. It requires a deep understanding of how Google evaluates trust, link patterns, and site behavior over time. That is where experience makes the difference.
At Stellar SEO, we have seen nearly every link-related issue possible, from large-scale negative SEO attacks to algorithmic devaluations that wiped out years of traffic. Because we have handled more than 100 recoveries and built over 25,000 quality links, we know how to separate harmless noise from genuine threats.
Inexperienced agencies often rely on automated tools and blanket disavow files that remove good links along with the bad. This approach destroys authority instead of protecting it. We take a targeted, data-backed approach, disavowing only when necessary and rebuilding trust through earned placements that strengthen your authority profile.
Google’s algorithms change frequently, but one principle remains constant: credible links from relevant, high-quality sources create lasting visibility. Experience ensures you know which links help, which hurt, and which simply need better context, not removal.
Common Myths About Bad Backlinks
Backlinks are not fully understood by many domain owners, who may hold misconceptions about how link juice is determined.
One common myth is that nofollow links will have no repercussions and can be ignored. This was true in the past, but now the nofollow attribute is considered a hint or suggestion about a website’s quality. While you do not need to remove one or two bad nofollow backlinks, a large number of these links can result in lower rankings or reduced trust.
However, you should also not simply disavow anything that seems suspicious. Some low-value links offer additional benefits, such as increased referral traffic, without compromising your authority. Disavowing numerous links simultaneously can also appear suspicious to search algorithms.
Our SEO experts can review your profile and determine which actions will most benefit your SEO without causing any penalties.
FAQs About Bad Backlinks
What qualifies as a bad backlink?
A bad backlink could reduce your ranking or damage your reputation. This can include excessive links from forums, links from low-quality directories, or links from a hacked site.
Should I disavow nofollow spam links?
Links with the nofollow attribute will not harm your rankings. However, after the Penguin update, Google announced that it considers nofollow links as “hints” about a website’s quality.
If you have one or two suspicious nofollow backlinks, this may not cause problems. However, if there is a high number of nofollow spam links, consider disavowing them.
Can bad backlinks hurt a new website?
Yes, bad backlinks can be especially harmful to a new website. More established sites will have a robust backlink profile and will not take as much of a hit from a few suspicious links. However, new websites have not yet established a diverse link profile, making them more susceptible to harmful backlinks.
If you are just starting with SEO and notice toxic backlinks, reach out to us to learn more about how we can protect your reputation.
How fast can I recover from a link penalty?
The recovery period depends on what type of penalty you received. A manual penalty can typically be resolved within a few months, but algorithmic penalties may take much longer.